Nickel: The Critical Metal Powering The Future Of Energy, But Are We Running Out?

Introduction to Critical Metals
In the quest for a sustainable future, the world is shifting gears towards cleaner, renewable sources of energy. This transition, however, is not just about harnessing the power of natural sources like the wind, sun, or water. It’s also about understanding what materials make this transformation possible. Among these materials is a group known as ‘critical metals,’ which play a pivotal role in the energy transition.
Critical metals are a group of elements that are essential to the manufacturing of high-tech devices, military equipment, and green technologies, among other applications. Their growing importance has led them to be deemed critical, notably because of the lack of current domestic production levels. These metals include elements like lithium, cobalt, rare earth elements, and of course, nickel.
Nickel, in particular, has emerged as a crucial player in the clean energy transition. Its unique properties, including high melting point, resistance to corrosion and oxidation, and excellent conductivity, make it indispensable in various industries; if it’s made of stainless steel, it’s got nickel in it. But it’s the role of nickel in the production of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy technologies that has truly catapulted it into the spotlight. The anticipated demand for EVs put unparalleled pressure on the need for nickel, in a way that is not achievable with current domestic supply levels.
In the following sections, we delve deeper into the world of nickel: its role in the current state of domestic US supply sources, future demand and potential solutions. As we navigate through these topics, we uncover why nickel is not just a metal, but a critical resource that could shape the future of our planet.
Focus on Nickel
Ever wondered why nickel is so important? Why is it considered a critical metal? Let’s find out.
Nickel. It’s more than just a five-cent coin. This silvery-white, lustrous metal is a real game-changer in the world of technology and energy. But what makes it so special?
First, let’s talk about its properties. Nickel is tough. It has a high melting point and is resistant to corrosion and oxidation. This means it can withstand extreme conditions and last a long time.
But that’s not all. Nickel is a superb conductor of heat and electricity. This makes it a key player in a broad range of industries, from stainless steel production to electronics manufacturing.
Now, let’s shift gears and talk about its role in clean energy. You see, nickel has a starring role here too. It’s a vital component in the manufacture of lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles and store renewable energy. Without nickel, the green energy revolution we’re all hoping for might just not happen at the speed it needs to. Pretty impressive right?
So, nickel is a big deal. But, like all good things, it’s not unlimited. And that’s where things get tricky.
The properties of nickel facilitate the deployment of the entire spectrum of clean energy technologies – geothermal, batteries for EVs and energy storage, hydrogen, hydro, wind and concentrating solar power. It is also necessary in nuclear energy technologies as well as carbon capture and storage.Nickel Institute
Nickel in Clean Energy Transitions
Have you ever stopped to think about what powers your phone, your computer, your power tools, and now your electric car or the renewable energy systems we’re increasingly relying on? The answer lies in a widely used component, the lithium ion battery. And guess what’s at the heart of these batteries? That’s right, it’s our superstar – Nickel.
Why nickel, you ask? Well, nickel-based lithium-ion batteries, contain more nickel than lithium, have a higher energy density and storage capacity compared to other types of batteries. That means they can store more energy and run for longer periods. Imagine your electric car running extra miles without needing a recharge. Sounds great, doesn’t it?
But it’s not just about electric cars. Nickel is also crucial in the renewable energy sector. Energy storage systems, which are essential for harnessing and utilizing power from renewable sources like wind and solar, heavily depend on nickel-based batteries. Without nickel, these systems wouldn’t be nearly as efficient or reliable.
So, it’s clear that nickel is a linchpin in our transition to clean energy. But here’s the million-dollar question: Do we have enough domestic nickel to support this transition?
Overall supply and demand of nickel for batteries by sector, 2016-2022
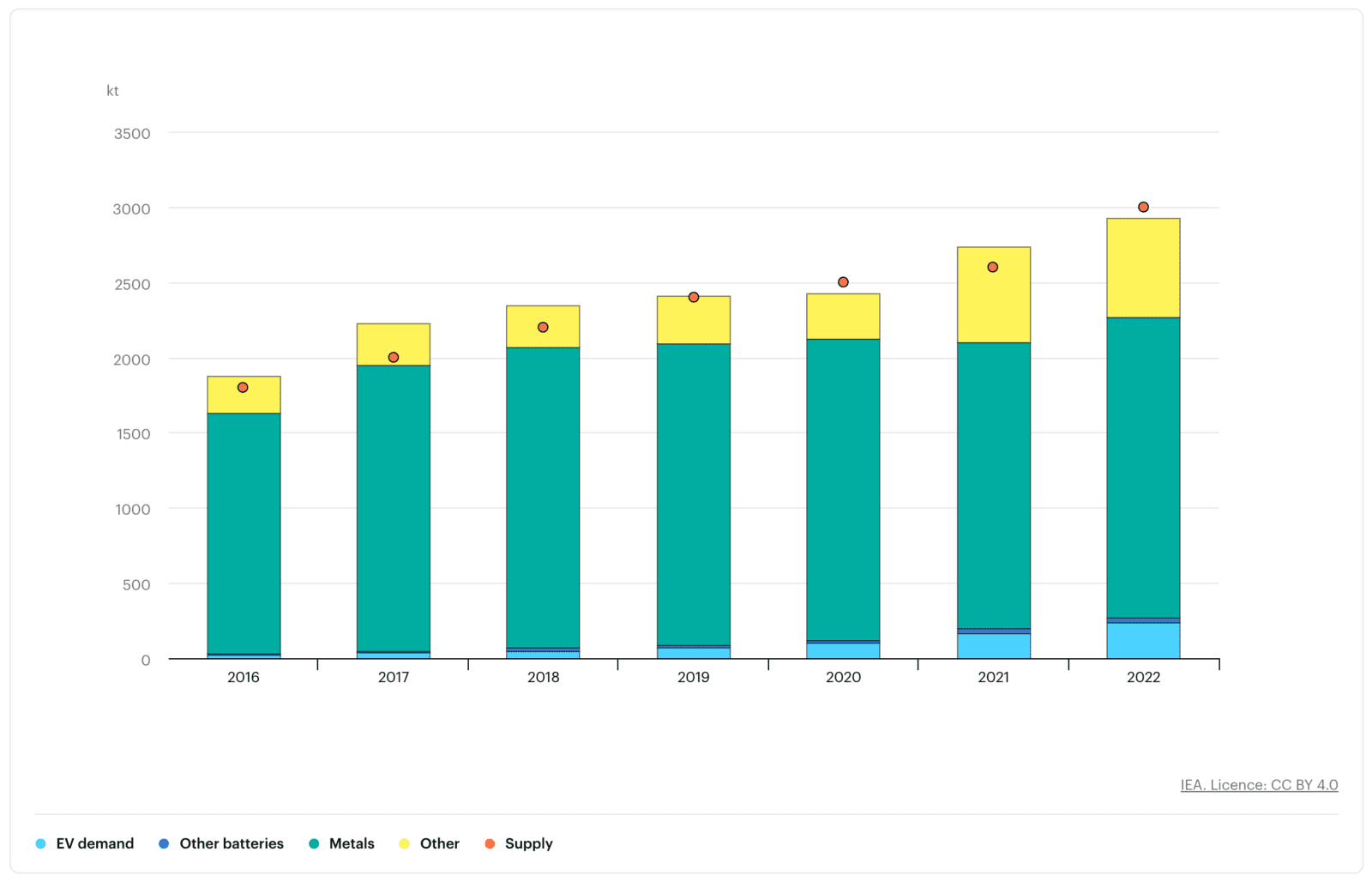
IEA, Overall supply and demand of nickel for batteries by sector, 2016-2022, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/overall-supply-and-demand-of-nickel-for-batteries-by-sector-2016-2022, IEA. Licence: CC BY 4.0
Current State of Nickel Supply
Let’s take a moment to understand the global nickel supply. But where is all this nickel coming from? In 2022, the world’s primary nickel demand is expected to grow by a whopping 17%, following a 4.8% increase in 2021.
One source lies mainly in Indonesia, which has emerged as the world’s largest producer of nickel. Other major nickel-producing countries include Indonesia, the Philippines, Russia, New Caledonia, and Australia. In fact, Asia accounted for a staggering 83.5% of global primary nickel usage in 2021, reinforcing its critical need for primary nickel deposits in the US.
But let’s delve a little deeper into these major players:
- Indonesia: Home to the world’s largest known nickel reserves and the top producer of nickel.
- Philippines: A significant player in the global nickel production scene.
- Russia: Another heavyweight in the world of nickel production.
- New Caledonia: A key contributor to the global nickel supply.
- Australia: Known for its substantial nickel reserves and production.
However, the nickel supply chain isn’t without its challenges. Nickel mining raises serious environmental and social concerns, including pollution, indigenous rights issues, greenhouse gas emissions, and working conditions.
Particularly in Indonesia it’s an energy-intensive process to break the chemical bonds to separate and recover the nickel metal when it’s in oxide form. Unfortunately coal is often burned to liberate the nickel. This processing is counterproductive to the move to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by converting to battery power for vehicles
Moreover, the dominance of nickel production by certain countries, such as Indonesia, presents both environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks and single-source risks. While Indonesia is the largest producer, it holds only 21% of global nickel reserves, highlighting the need for diversification.
Interestingly, the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) has moved nickel up the list on the critical metal list and is actively making investments in North American Nickel companies.
So, while nickel production is on the rise, it’s clear that we need to address these challenges to ensure a sustainable and secure nickel supply for our clean energy future.
Future Demand and Supply Challenges
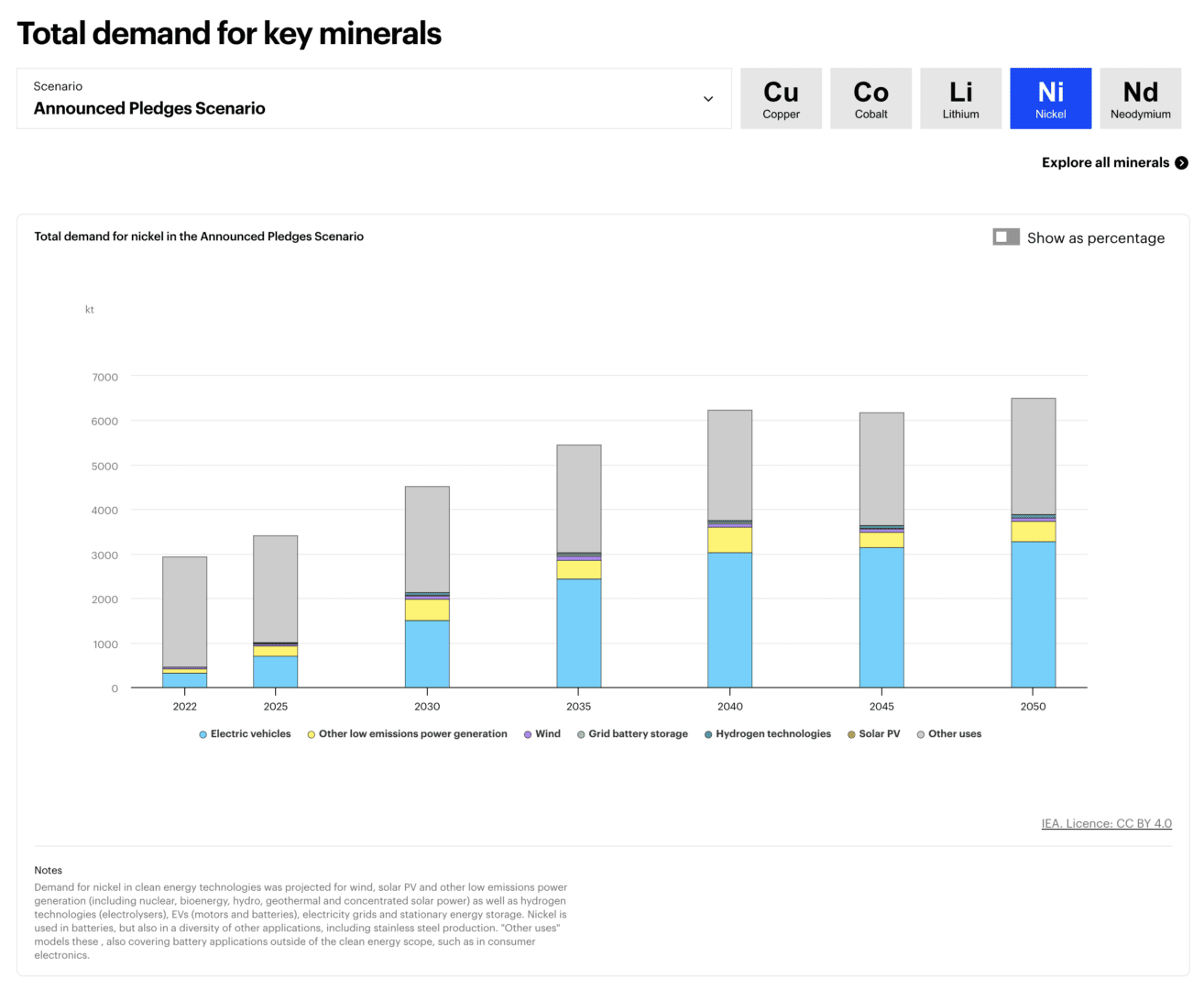
So, we’ve established that nickel is crucial for our clean energy future. But can we meet the skyrocketing demand?
Predictions show that the demand for nickel in batteries alone could increase tenfold from 2020 to 2040. Now, that’s a lot of nickel! But will we have enough to meet this demand?
Unfortunately, the answer isn’t straightforward. Nickel mining is a complex process, fraught with environmental and social challenges. Plus, the majority of nickel reserves are concentrated in a few countries, which raises geopolitical concerns.
And here’s another curveball. Not all nickel can be used in batteries.
Only certain types of high-purity nickel are suitable, and producing this high-grade nickel is costly and energy-intensive.
So, we’re facing a potential crunch point. The demand for nickel is set to soar, but supply challenges could put a spanner in the works.
Solutions and Alternatives
Faced with these challenges, what can we do to secure our nickel supply?
- Find low-cost domestic environmentally safe sources.
Unfortunately, there are a mere handful of high quality, high grade deposits being developed in North America. Existing nickel mines are aging and playing out. For investors who want to take advantage of the EV battery-driven demand trend, North American pure-play nickel deals are hard to find for development and for investors who want to take advantage of this trend.
- Another
Currently, only a small fraction of nickel in end-of-life batteries is recycled. By improving recycling technologies and infrastructure, we could recover more nickel and reduce our reliance on mining. Yet this is proving difficult to do. Metals need to be cycled first before they can be recycled.
- Lastly, policy and technology will play a crucial role.
Governments and companies need to invest in sustainable mining practices on the right resource development projects. In North America, we have the highest standards for environmental protection and human resources. For supply chain security and for environmental protection, it makes sense to mine nickel and other critical metals domestically.




